Textiles

01
Coatings
When textiles and foils are coated, a polymeric layer is applied directly to one or both surfaces of the fabric. A range of organic solvents (MEK-methyl ethyl ketone), but also dimethylformamide (DMF) and toluene (both are non-ESIG solvents) are involved depending on the coating polymer type specified to prepare the polyurethane coating mixtures. The coating or lamination improves functional performance properties such as thermo-plasticity, adhesion, abrasion resistance, heat, water and air conductivity, or ultraviolet (UV) radiation resistance of the finished products which can be technical and medical textiles, protective clothing or mattress covers.

02
Adhesives
Contact adhesives are probably the best-known solvent-based adhesives. The adhesive is a polymer solution in organic solvents such as ketones, ethyl acetate, or a hydrocarbon solvent applied to both surfaces to bond. Some time is allowed for the solvent to evaporate, and the surfaces are then pressed together. Solvent-based adhesives are used widely for bonding to leathers, nylons, PVC, polyurethane or rubbers, which are all common materials used, for instance, for footwear soles.

03
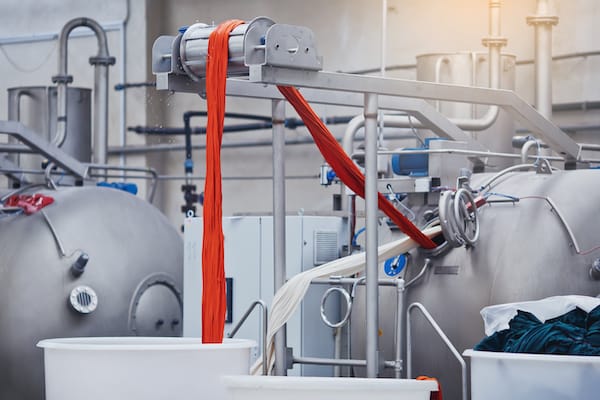
Dyes
Glycol ethers are used as additives during the textile dyebath to obtain properties such as proper shade, level dyeing, colourfastness, reduced dyeing temperatures and reduced dyeing cycle times. They help the dyes penetrate and saturate the fabric, accelerating the dyeing process. They also serve as couplers for other components of the dye formulation and can act as compatibilising agents for fabric blends such as nylon/acrylics.

04
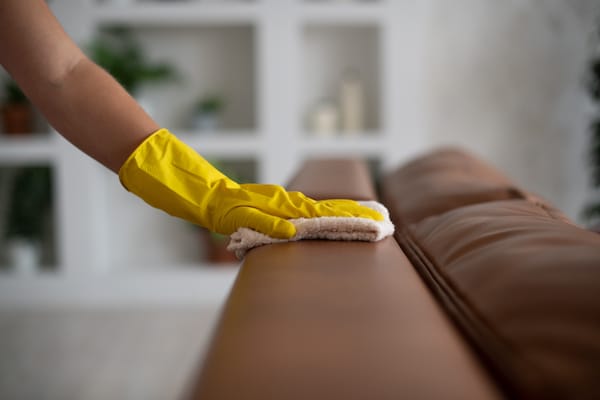
Cleaning & leather degreasing
In dry cleaning, aliphatic hydrocarbon solvents and glycol ethers are used to clean fabrics that degrade in water and delicate fabrics that cannot withstand the rough and tumble of a washing machine and clothes dryer.
When it comes to leather, solvent-based cleaners will effortlessly remove dye transfer without damaging the leather’s protective sealant or removing colour. It will also remove stains like fresh ink, grease or oil marks from leather.
Stain removers contain hydrocarbon solvents. Both solvents and greasy stains are non-polar substances. This similar characteristic enables the stain remover to seep under the stain and effectively break it down without harming the fabric.